Introduction
Aluminum extrusion dies and tooling are critical components in the aluminum extrusion process, shaping molten aluminum into complex profiles and shapes.
Understanding the design, materials, manufacturing process, and maintenance of extrusion dies and tooling is essential for optimizing extrusion operations and achieving high-quality results.
This comprehensive guide provides insights into all aspects of aluminum extrusion dies and tooling.
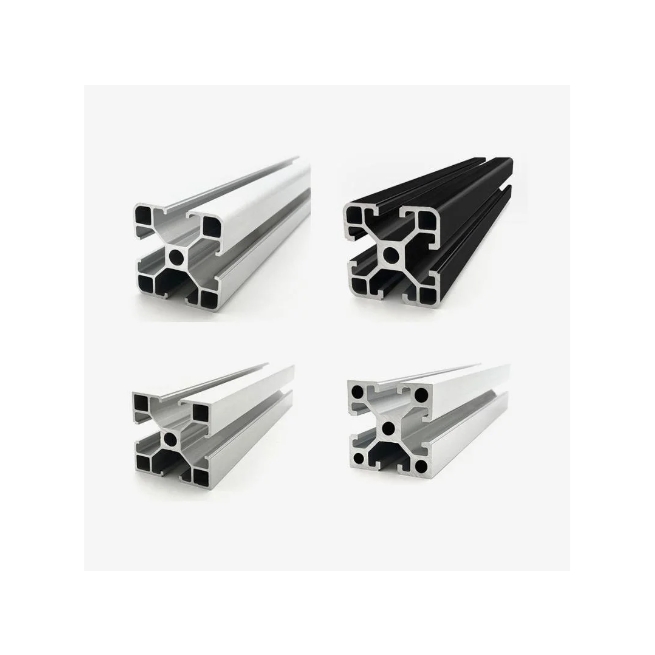


Design of Extrusion Dies
The design of extrusion dies involves several considerations to ensure efficient material flow, dimensional accuracy, and structural integrity of extruded profiles.
Key factors in die design include:
| Aspect | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Profile Geometry | The shape and dimensions of the extruded profile dictate the design of the die cavity, including cross-sectional features, tolerances, and surface finish requirements. | High |
| Die Land and Back Relief | Critical elements controlling metal flow and pressure distribution within the die cavity, minimizing die wear and improving extrusion quality. | High |
| Temperature Control | Effective temperature control through cooling channels or heating elements is essential to maintain uniform material flow and prevent premature die failure. | High |
Materials for Extrusion Dies
Extrusion dies are typically made from high-strength tool steels or carbide materials to withstand the high pressures and temperatures encountered during the extrusion process.
Common die materials include:
- H13 Tool Steel: H13 tool steel offers excellent thermal conductivity, wear resistance, and toughness, making it suitable for high-volume extrusion applications.
- Carbide: Carbide materials such as tungsten carbide provide superior hardness and abrasion resistance, extending die life and reducing maintenance requirements.
- Cermet: Cermet materials combine ceramic and metallic elements to offer a balance of wear resistance, toughness, and thermal stability, ideal for extruding abrasive or high-temperature alloys.
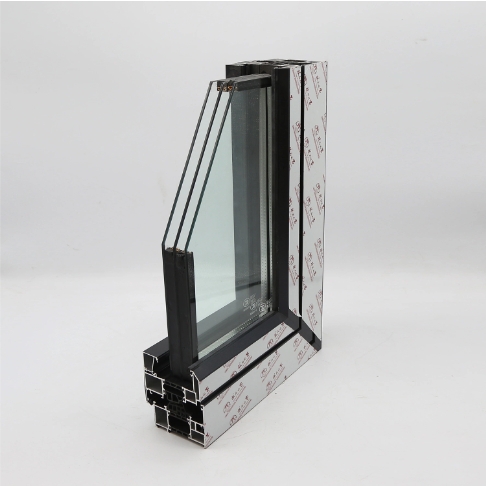



Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of extrusion dies involves several steps, including:
| Aspect | Description | Additional Details |
|---|---|---|
| Profile Geometry | The shape and dimensions of the extruded profile dictate the design of the die cavity, including cross-sectional features, tolerances, and surface finish requirements. | Determines the overall form and specifications of the extruded product. |
| Die Land and Back Relief | Critical elements controlling metal flow and pressure distribution within the die cavity, minimizing die wear and improving extrusion quality. | Designed to optimize material flow and reduce friction, ensuring uniform product quality. |
| Temperature Control | Effective temperature control through cooling channels or heating elements is essential to maintain uniform material flow and prevent premature die failure. | Maintains consistent temperature throughout the die, preventing distortion and defects in the extruded material. |
Maintenance and Optimization
Regular maintenance and optimization of extrusion dies and tooling are essential to prolong service life and maintain extrusion quality.
Maintenance tasks may include:
| Maintenance Task | Description | Professional Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Die Cleaning | Regular removal of extrusion residues, scale, and contaminants from die cavities to prevent buildup and maintain consistent material flow. | Utilize appropriate cleaning agents and methods to avoid damage to die surfaces. Regularly inspect and clean die vents to ensure proper venting. |
| Die Polishing | Periodic polishing of die surfaces to remove imperfections, scratches, or burrs that can affect profile finish and dimensional accuracy. | Use specialized polishing tools and techniques to achieve desired surface finishes without altering profile geometry. Perform polishing only when necessary to avoid excessive material removal. |
| Die Inspection | Scheduled inspections for wear, cracks, or deformation, with timely repair or replacement of worn components to prevent production interruptions and defects. | Implement a structured inspection schedule, including visual and dimensional checks. Utilize advanced inspection tools such as micrometers and bore gauges for accurate assessment. Regularly monitor die temperature and lubrication to prevent premature wear. |
Conclusion
Aluminum extrusion dies and tooling are integral to the extrusion process, influencing the quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of aluminum extruded products.
By understanding the design principles, materials, manufacturing process, and maintenance requirements of extrusion dies and tooling, manufacturers can optimize their extrusion operations and achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Drop me an email with your ideas, and I’ll get back to you swiftly!

















