In metal die casting, hot chamber and cold chamber die casting are two prevalent methods that fundamentally differ based on the metal’s melting point and the die casting machine’s design.
Hot chamber die casting is primarily used for metals with low melting points, such as zinc, magnesium, and tin. In this process, the injection system is immersed directly in the molten metal, thus earning the name “hot chamber.”
This technique is ideal for the fast production of small, precision parts; The high-temperature environment increases the equipment’s maintenance costs.
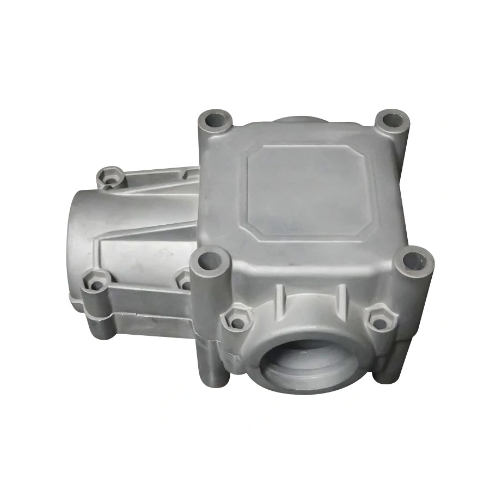
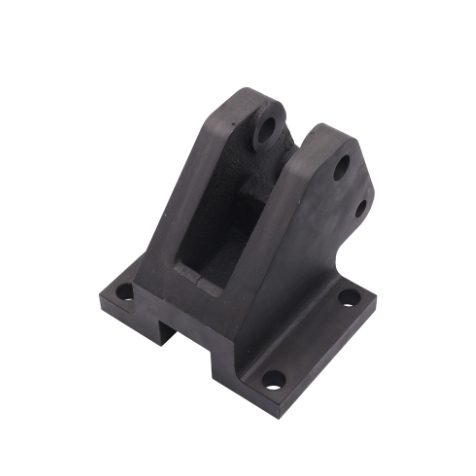
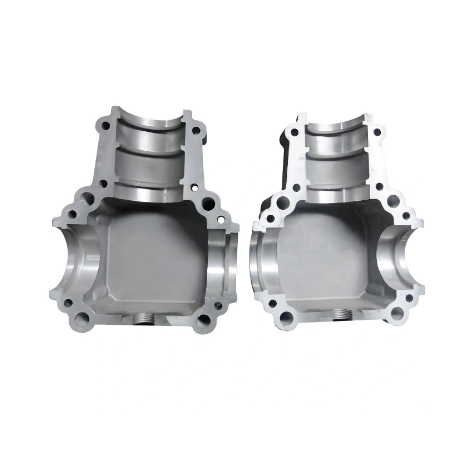



Conversely, cold chamber die casting is suited for metals with high melting points, like aluminum and copper.
In cold chamber die casting, the molten metal is heated in an external furnace and then either manually or automatically poured into the injection chamber.
This method’s advantage lies in its capability to handle metals at high temperatures, and it boasts more durable equipment.
Nonetheless, because the molten metal must be transferred from the furnace to the chamber, the production speed can be slower.

For aluminum die cast parts in automobiles, cold chamber die casting is generally used due to aluminum’s higher melting point.
This process can produce parts with excellent dimensional accuracy and greater strength and can also accommodate larger castings.
While it is relatively easy to perform and has lower maintenance costs, the cycle time may be slower than hot chamber die casting due to the external transfer of molten metal.
When choosing a die casting process, considerations should include the metal’s melting point, the product’s size, the complexity of its shape, and production efficiency.
Hot chamber die casting is favored for its high efficiency and superior surface finish of products, while cold chamber die casting is preferred for its suitability with high melting point metals and the production of larger parts.
Each method has its advantages and limitations, and the appropriate choice can significantly enhance production efficiency and product quality.
Contact us today to discuss your project needs and receive a quote, you can trust us to deliver exceptional castings that meet your requirements.

















